“PROMOTING ARTERIAL HEALTH:THE ROLE OF VITAMIN K AND NITRIC OXIDE IN ATHEROSCLEROSIS PREVENTION”
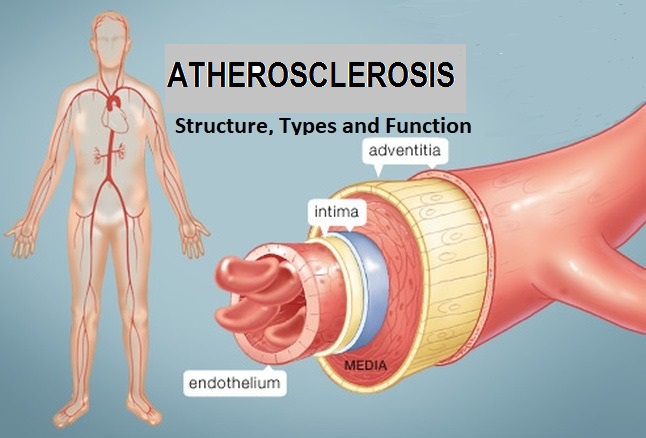
Atherosclerosis is a complex cardiovascular condition where fatty deposits, cholesterol, and other substances build up on the inner walls of arteries, forming plaques. These plaques can narrow and stiffen the arteries, restricting blood flow. Over time, inflammation, accumulation of immune cells, and calcification can occur within these plaques, making them unstable.
If a plaque ruptures, it can trigger blood clot formation, which can partially or completely block an artery. This can lead to various cardiovascular diseases, such as coronary artery disease (heart attacks) if it occurs in the coronary arteries, or strokes if it happens in the carotid or cerebral arteries.
Atherosclerosis often develops over years or decades and can be influenced by factors like diet, lifestyle, genetics, and underlying medical conditions like hypertension and diabetes.
Vitamin K Reduces Plaques:
Vitamin K plays a crucial role in reducing plaque by supporting proper blood clotting and promoting healthy arterial function. There are two main forms of vitamin K: K1 (phylloquinone) and K2 (menaquinone). Here’s a detailed explanation of how vitamin K helps reduce plaque:
Blood Clotting Regulation:
Vitamin K is essential for the production of certain proteins in the body called clotting factors. These proteins are responsible for helping the blood to clot when there’s an injury. Proper blood clotting prevents excessive bleeding, but it also has a connection to plaque reduction. When blood vessels are damaged due to factors like inflammation or high blood pressure, they become more susceptible to plaque buildup. Vitamin K ensures that blood clotting is balanced and controlled, preventing the formation of unwanted blood clots that could contribute to plaque formation.
Calcium Regulation:
Vitamin K2, in particular, plays a vital role in regulating calcium metabolism in the body. Calcium is necessary for bone health, but it can be problematic when it accumulates in arteries and other soft tissues. This buildup of calcium can contribute to the hardening and narrowing of arteries, a process known as arteriosclerosis or atherosclerosis. Vitamin K2 activates proteins that help guide calcium away from arterial walls and towards bones, where it’s needed for proper mineralization.
Matrix Gla Protein (MGP):
Matrix Gla Protein is a vitamin K-dependent protein that helps prevent the buildup of calcium in arterial walls. When vitamin K2 activates MGP, it becomes an inhibitor of calcification, ensuring that calcium doesn’t accumulate in arteries and contribute to plaque formation. Research has shown that a deficiency in vitamin K2 can lead to inadequate activation of MGP, potentially increasing the risk of arterial calcification.
Inflammation Reduction:
Chronic inflammation is a key factor in the development of plaque. Vitamin K has anti-inflammatory properties that help mitigate the inflammatory response within blood vessels. By reducing inflammation, vitamin K indirectly contributes to reducing the risk of plaque formation.
It’s important to note that while vitamin K is beneficial for reducing plaque, it’s just one piece of the puzzle. A healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced diet, regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding smoking is crucial for overall cardiovascular health. Additionally, individuals taking blood-thinning medications (anticoagulants) should consult their healthcare provider before making significant changes to their vitamin K intake, as it can interact with these medications.
NO: Reducing Atherosclerosis Naturally:
Atherosclerosis is a condition where plaque builds up in your arteries, causing them to narrow and harden. Nitric oxide (NO) is a molecule that plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy blood vessels and reducing the risk of atherosclerosis. Here’s how it works in detail:
Vasodilation:
Nitric oxide helps relax and dilate blood vessels, improving blood flow and reducing the strain on the arterial walls. This prevents the damage that can lead to plaque formation.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects:
Nitric oxide has anti-inflammatory properties that help reduce the inflammation associated with the early stages of atherosclerosis. This prevents immune cells from accumulating in the artery walls and forming plaque.
Platelet Inhibition:
Nitric oxide helps prevent platelets from sticking together and forming blood clots. Blood clots can lead to artery blockages, which can trigger heart attacks or strokes.
Cholesterol Regulation:
Nitric oxide helps regulate cholesterol levels by reducing the uptake of LDL cholesterol (the “bad” cholesterol) into the artery walls. This reduces the formation of fatty plaques.
Antioxidant Activity:
Nitric oxide acts as an antioxidant, neutralizing harmful free radicals that can damage the arterial walls and contribute to plaque formation.
How to enhance nitric oxide production to reduce atherosclerosis:
Healthy Diet:
Consume foods rich in nitrates, such as leafy greens, beets, and pomegranates. These foods can be converted to nitric oxide in the body.
Exercise:
Regular physical activity stimulates the production of nitric oxide. Both aerobic and resistance exercises have been shown to improve nitric oxide levels.
Adequate Sleep:
Prioritize quality sleep, as sleep deprivation can reduce nitric oxide production.
Avoid Smoking:
Smoking reduces nitric oxide bioavailability, so quitting smoking can help improve its levels.
L-arginine:
This amino acid is a precursor to nitric oxide. Foods rich in L-arginine include nuts, seeds, legumes, and seafood.
Antioxidant-Rich Diet:
Consume foods rich in antioxidants, such as berries, citrus fruits, and dark leafy greens. Antioxidants help preserve nitric oxide activity.
Limit Processed Foods:
High intake of processed foods, saturated fats, and added sugars can impair nitric oxide production and contribute to atherosclerosis.
Manage Stress:
Chronic stress can negatively affect nitric oxide production. Engage in stress-reduction techniques like meditation, deep breathing, or yoga.
Remember that a holistic approach involving multiple lifestyle changes is the most effective way to enhance nitric oxide production and reduce the risk of atherosclerosis.
S P E C I A L .
The production of Nitric Oxide diminishes as we age .We will have to enhance Nitric Oxide with the help of dietary material.
- The production of Nitric oxide is 100% up to the age of 20 yr.
- The production of Nitric oxide diminishes by 40 % at the age of 40 yr.
3.The product of of Nitric oxide diminishes by 50% at the age of 50 yr.
4.The production of Nitric oxide diminishes by 85% at the age of 60 yr.
- The vitamin K is very helpful to reduce plaque . Include Spinach and Beetroot in your diet.
FAQ on Atherosclerosis:
Q-What are Measures to prevent artrial plaque?
A-Preventing arterial plaque buildup involves adopting a healthy lifestyle. You can focus on maintaining a balanced diet, regular exercise, not smoking, managing stress, and controlling conditions like high blood pressure, cholesterol, and diabetes.
Q-What are the food to enhanance nitric oxide?
A-Foods that can help enhance nitric oxide production include leafy greens (like spinach and kale), beets, garlic, and citrus fruits.
{NUTRITION LIFE CIRCLE} 

My Self Hari singh choudhary
S.N.H.S. Dip.(Holistic nutrition), London, S.N.H.S. Dip. (Advanced Nutrition), London, S.N.H.S. Dip. (Holistic Pain Management), London, S.N.H.S. Dip. (Nutrition for Age 50+), London, S.N.H.S. Dip. (Plant-Based Nutrition), London, S.N.H.S. Dip. (Vegetarian & Vegan Nutrition,) London, Certified Diabetes Educator’s (INDO-VIETNAM MEDICAL BOARD, Associate member of The International College of Holistic Medicine, England.
NATURAL DISEASE ERADICATION
[ NUTRITION THERAPY ]
For Business inquiry:-
Email: nutritionlifecircle@gmail.com
WhatsApp Number: +91 9425090558