“NATURES SECRET TO GUT HAPPINESS: EXPLORING PREBIOTICS AND PROBIOTICS”
PROBIOTICS:
Probiotics are live microorganisms, primarily bacteria and sometimes yeast, that are believed to provide various health benefits when consumed in adequate amounts. These beneficial microorganisms are often referred to as “good bacteria” and are naturally present in the human digestive system. Probiotics can also be found in certain foods and supplements.
Probiotics function by maintaining a balanced microbial environment in the gut, which is crucial for digestion, nutrient absorption, and overall immune system health. They help inhibit the growth of harmful bacteria, support the integrity of the intestinal lining, and play a role in producing certain vitamins and nutrients.
Different strains of probiotics offer different potential benefits. Some common benefits associated with probiotics include:
Improved Digestion:
Probiotics can aid in breaking down food and enhancing the absorption of nutrients, which can help alleviate digestive issues such as bloating, gas, and diarrhea.
Enhanced Immune Function:
A significant portion of the immune system is located in the gut. Probiotics may help modulate immune responses and protect against infections by promoting a healthy gut environment.
Gut Health:
Probiotics contribute to the balance of gut bacteria, which can impact overall gut health and reduce the risk of conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
Mental Health:
There is emerging research suggesting a link between gut health and mental well-being. Probiotics might have a role in reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression.
Skin Health:
Some evidence suggests that certain probiotics can influence skin health by reducing inflammation and improving conditions like eczema.
Probiotics can be found in various food sources, such as yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, and kombucha. Additionally, they are available in the form of dietary supplements. When choosing a probiotic supplement, it’s important to consider factors such as the specific strains included, the colony-forming units (CFUs) count, and any potential allergies or sensitivities.
It’s worth noting that while probiotics have shown promise in various areas, more research is needed to fully understand their mechanisms of action and the specific benefits they offer.
PROBIOTIC FOUND NATURALLY:
Probiotics are naturally found in fermented foods such as
yogurt.
kefir.
sauerkraut.
kimchi.
and certain types of cheese.
They can also be taken in the form of supplements.
HOW IT CAN CONSUME :
Probiotics can be consumed through foods like yogurt and fermented vegetables, or by taking dietary supplements. It’s important to follow recommended dosage instructions for supplements.
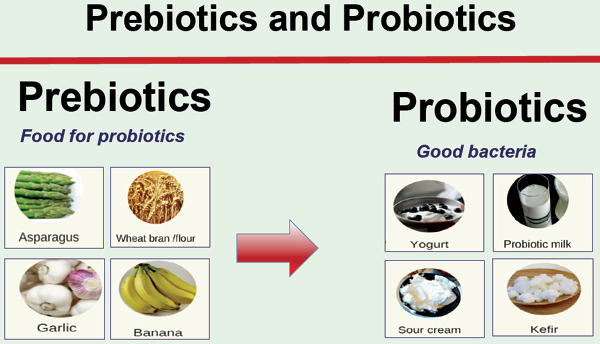
PREBIOTICS:
Prebiotics are non-digestible dietary fibers that serve as nourishment for beneficial bacteria in the gut. They are a type of functional food component that helps promote the growth and activity of these beneficial microorganisms, primarily in the colon.
PREBIOTIC IS NON LIVINING:
Unlike probiotics (live beneficial bacteria), prebiotics are not living organisms themselves. Instead, they are complex carbohydrates, mainly oligosaccharides, which are resistant to digestion by human enzymes in the upper gastrointestinal tract. This means they reach the colon largely intact, where they become a source of energy for certain strains of bacteria.
The fermentation of prebiotics by these bacteria produces short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), such as acetate, propionate, and butyrate. SCFAs are essential for maintaining the health of the colon cells and have various positive effects on the body. They help regulate pH levels, increase mineral absorption (especially calcium and magnesium), and support the integrity of the gut barrier, which can aid in preventing the passage of harmful substances into the bloodstream.
In addition to promoting gut health, prebiotics have been linked to several potential health benefits, including improved digestion, enhanced immune function, and even potential effects on metabolic health. Foods rich in prebiotics include certain types of fiber-rich vegetables (like onions, garlic, leeks, asparagus, and Jerusalem artichokes), fruits (such as bananas), whole grains, and legumes.
SUMMARY:
prebiotics are specialized dietary Fibers that feed beneficial bacteria in the gut, promoting their growth and activity. They play a crucial role in supporting gut health, improving digestion, and potentially offering other health benefits.
Remember that while both prebiotics and probiotics are beneficial for gut health, they serve different purposes. Probiotics introduce live beneficial bacteria into your gut, while prebiotics provide the necessary nourishment for these bacteria to thrive.
S P E C I A L .
1.Anti-biotics are the enemies of good gut
bacteria.don’t use frequently .your
Probiotics became lost.
2.Prebiotics are the food for probiotics.
3.Probiotics are the living organisms.they need prebiotic to survived.
4.Prebiotics are non-digestible Fiber fewere. scientifically known as
1.Insulin.
2.fructooligosaccharides.
3.galactooligosaccharides.
5.To promote ultimate growth of good bacteria and gut health we need probiotics As well as Prebiotics.
FAQ Prebiotics:
Q-What are prebiotics?
A-Prebiotics are non-digestible Fibers and compounds found in certain foods that promote the growth and activity of beneficial bacteria in the gut.
Q-How do prebiotics work?
A-Prebiotics serve as a food source for probiotics (good bacteria) in the gut, helping them to flourish and maintain a healthy balance of the gut microbiota.
Q-What foods are high in prebiotics?
A-Foods like garlic, onions, bananas, asparagus, chicory root, and whole grains contain prebiotic Fibers.
Q-What are the health benefits of prebiotics?
A-Consuming prebiotics can improve digestion, support the immune system, and potentially contribute to weight management.
Q-What are probiotics?
A-Probiotics are live microorganisms, mainly bacteria and some yeasts, that provide health benefits when consumed in adequate amounts. They are often referred to as “good” or “friendly” bacteria.
Q-How do probiotics impact gut health?
A-Probiotics help maintain a balanced gut microbiota, supporting digestion, nutrient absorption, and immune function.
Q-What are some sources of probiotics?
A-Common sources include yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, miso, and certain dietary supplements.
Q-What are the potential benefits of probiotics?
A-Probiotics may help alleviate digestive issues, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and support overall gut health. Some strains might also have immune-boosting properties.
Q-Can everyone benefit from probiotics?
A-While probiotics can be beneficial for many people, individual responses vary. Consult a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen, especially if you have underlying health conditions.
Remember, maintaining a healthy gut involves a combination of factors, including a balanced diet rich in Fiber and whole foods, regular exercise, and managing stress.
{NUTRITION LIFE CIRCLE} 

My Self Hari singh choudhary
S.N.H.S. Dip.(Holistic nutrition), London, S.N.H.S. Dip. (Advanced Nutrition), London, S.N.H.S. Dip. (Holistic Pain Management), London, S.N.H.S. Dip. (Nutrition for Age 50+), London, S.N.H.S. Dip. (Plant-Based Nutrition), London, S.N.H.S. Dip. (Vegetarian & Vegan Nutrition,) London, Certified Diabetes Educator’s (INDO-VIETNAM MEDICAL BOARD, Associate member of The International College of Holistic Medicine, England.
NATURAL DISEASE ERADICATION
[ NUTRITION THERAPY ]
For Business inquiry:-
Email: nutritionlifecircle@gmail.com
WhatsApp Number: +91 9425090558