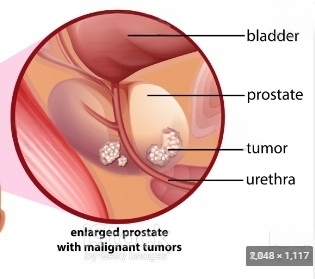
Prostate Cancer:
Prostate cancer is a type of cancer that develops in the prostate, a small gland located below the bladder in males. The prostate gland is responsible for producing seminal fluid, which nourishes and transports sperm. Prostate cancer occurs when cells in the prostate gland begin to grow and divide abnormally, forming a tumor.
Cause of prostate cancer:
The exact cause of prostate cancer is unknown, but several factors can contribute to its development. These factors include age (the risk increases with age), family history of prostate cancer, ethnicity (African-American men are at higher risk), and certain genetic changes.
Prostate Cancer and treatment:
There are various treatment options for prostate cancer, depending on the stage and aggressiveness of the cancer. These can include:
Active surveillance:
For slow-growing or early-stage prostate cancer, doctors may recommend monitoring the cancer closely without immediate treatment.
Surgery:
The surgical removal of the prostate gland, known as a prostatectomy, may be recommended for localized or early-stage prostate cancer.
Radiation therapy:
High-energy beams are used to kill cancer cells or stop their growth. Radiation therapy can be delivered externally (external beam radiation) or internally (brachytherapy).
Hormone therapy:
Prostate cancer cells often rely on male hormones, such as testosterone, to grow. Hormone therapy aims to lower hormone levels or block their effects, slowing down the cancer’s progression.
Chemotherapy:
This treatment uses drugs to kill cancer cells throughout the body. It is typically reserved for advanced cases of prostate cancer that have spread to other parts of the body.
Immunotherapy:
This approach stimulates the body’s immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells.
Targeted therapy:
Certain medications can target specific genetic mutations or abnormalities in cancer cells, inhibiting their growth.
Diet and prostate cancer:
Regarding diet, although no specific diet can cure prostate cancer, certain dietary habits may lower the risk of developing prostate cancer or help manage the condition. These dietary recommendations include:
Eating a balanced diet:
Consume a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Focusing on plant-based foods:
Include a good amount of fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains in your diet.
Limiting red and processed meats:
Reduce the consumption of red meat (such as beef, pork, and lamb) and processed meats (such as sausages, hot dogs, and bacon).
Choosing healthy fats:
Opt for sources of healthy fats, such as nuts, seeds, avocados, and olive oil, while limiting saturated and trans fats.
Consuming adequate calcium:
Get enough calcium from low-fat dairy products or non-dairy alternatives, as some studies suggest a link between high calcium intake and prostate cancer.
Staying hydrated:
Drink plenty of water and limit sugary beverages.
It’s important to note that dietary changes alone are not a cure for prostate cancer, but they can support overall health and potentially reduce the risk of developin hng the disease.
Lycopene & Cancer:
Lycopene is a naturally occurring compound that belongs to the carotenoid family, which is responsible for giving fruits and vegetables their red, orange, and yellow colors. Lycopene is most commonly associated with tomatoes and tomato-based products.
Regarding its potential effects on cancer cells, several studies have investigated the relationship between lycopene intake and cancer risk. While the results are not definitive and more research is needed, some studies have suggested potential benefits of lycopene in reducing the risk of certain types of cancer. Here are some key findings:
Prostate cancer:
Some observational studies have found an association between higher lycopene intake and a reduced risk of prostate cancer. However, clinical trials specifically examining the effects of lycopene on prostate cancer progression or treatment have shown mixed results.
It’s important to note that while some studies have shown potential benefits of lycopene, the evidence is not yet conclusive. Additionally, the effects of lycopene on cancer cells may vary depending on individual factors such as dosage, bioavailability, and interaction with other compounds in the diet.
SPECIAL :
Lycopene and prostate cancer. Tomato contain lycopene. when we prepare soup ,effect of lycopene increase by ten times.research shows when a person have one to two cup of tomato soup twice in a week,can reduce prostate cancer by 58%.use this to over come from prostate cancer.
FAQ on cure of prostate cancer.
Q: Is there a cure for prostate cancer?
A: Currently, there is no known cure for prostate cancer. However, various treatment options are available that can effectively manage the disease and extend a patient’s lifespan. The choice of treatment depends on several factors, including the stage of cancer, the patient’s overall health, and individual preferences.
Q: Are there any experimental or emerging treatments for prostate cancer?
A: Yes, there are several experimental or emerging treatments being studied for prostate cancer. These include:
Precision Medicine:
This approach involves analyzing a patient’s genetic makeup and other characteristics to develop personalized treatments.
Therapeutic Vaccines:
Vaccines that stimulate the immune system to recognize and destroy prostate cancer cells are being researched.
Radiopharmaceutical Therapy:
This treatment uses radioactive substances to target and destroy cancer cells while minimizing damage to healthy tissues.
Focal Therapy:
This technique aims to treat only the tumor area while sparing the rest of the prostate, potentially reducing side effects.
Gene Therapy:
Researchers are exploring the use of gene therapy to deliver specific genes or genetic material to prostate cancer cells, altering their behavior or killing them.
It’s important to note that these treatments may still be in clinical trials and require further research before becoming widely available.
Q: Can early detection improve the chances of a cure for prostate cancer?
A: Early detection of prostate cancer through regular screenings, such as prostate-specific antigen (PSA) tests and digital rectal exams (DREs), can increase the chances of successful treatment. Detecting prostate cancer at an early stage when it is localized or confined to the prostate gland offers more treatment options and potentially higher cure rates. Regular screenings are particularly important for men at higher risk, such as those with a family history of prostate cancer or African American men.
Q: How can I reduce the risk of developing prostate cancer?
A: While it is not possible to completely eliminate the risk of developing prostate cancer, certain lifestyle choices may help reduce the risk:
Maintain a healthy diet:
Consume a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Limit the intake of red and processed meats.
Stay physically active:
Engage in regular physical activity and exercise. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity activity per week.
Maintain a healthy weight:
Keep your body weight within a healthy range and avoid obesity.
Don’t smoke:
If you smoke, consider quitting. Smoking has been linked to an increased risk of developing aggressive forms of prostate cancer.
Discuss screening options:
Talk to your doctor about the benefits and risks of prostate cancer screening. The decision to undergo screening should be based on individual factors and preferences.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice based on your specific circumstances.
(Nutrition Life Circle) 

My Self Hari singh choudhary
S.N.H.S. Dip.(Holistic nutrition), London, S.N.H.S. Dip. (Advanced Nutrition), London, S.N.H.S. Dip. (Holistic Pain Management), London, S.N.H.S. Dip. (Nutrition for Age 50+), London, S.N.H.S. Dip. (Plant-Based Nutrition), London, S.N.H.S. Dip. (Vegetarian & Vegan Nutrition,) London, Certified Diabetes Educator’s (INDO-VIETNAM MEDICAL BOARD, Associate member of The International College of Holistic Medicine, England.
NATURAL DISEASE ERADICATION
[ NUTRITION THERAPY ]
For Business inquiry:-
Email: nutritionlifecircle@gmail.com
WhatsApp Number: +91 9425090558