“THE SECRETS OF CHRONIC INFLAMMATION:CAUSES AND HOLISTIC REMEDIES”
Chronic inflammation :
Chronic inflammation is a prolonged and sustained inflammatory response within the body that lasts for weeks, months, or even years. Unlike acute inflammation, which is a short-term and necessary process in the body’s defense against infection and injury, chronic inflammation is characterized by a persistent activation of the immune system that can have detrimental effects on tissues and organs.
Here’s a more detailed description:
Causes:
Chronic inflammation can be triggered by various factors, including infections, autoimmune disorders, exposure to irritants (such as smoking or pollution), obesity, and long-term exposure to stress.
Immune Response:
When the body detects a threat or injury, it releases pro-inflammatory molecules like cytokines and white blood cells to the affected area. In acute inflammation, this response is temporary and helps heal the body. In chronic inflammation, this response persists and becomes harmful.
Cellular Changes:
Over time, chronic inflammation can lead to changes in the cells of affected tissues. For example, it may cause tissue damage, scarring, and abnormal cell growth, which can contribute to the development of diseases like cancer.
Associated Diseases:
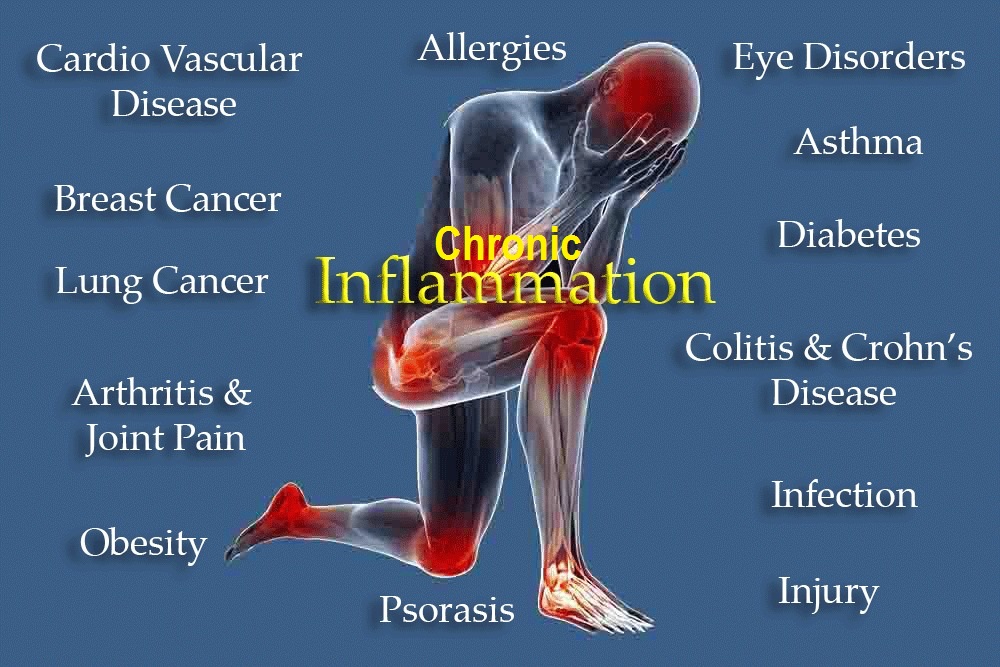
Chronic inflammation is associated with a wide range of health conditions, including cardiovascular diseases (atherosclerosis), diabetes, autoimmune disorders (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis), neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., Alzheimer’s), and certain cancers.
Symptoms:
Symptoms of chronic inflammation can vary depending on the affected organs but may include fatigue, pain, fever, and swelling. However, chronic inflammation can also be “silent” and not produce obvious symptoms.
Diagnosis and Treatment:
Diagnosing chronic inflammation often involves assessing specific markers in blood tests, like C-reactive protein (CRP) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). Treatment aims to address the underlying cause, such as managing autoimmune conditions, treating infections, or adopting a healthier lifestyle. Anti-inflammatory medications may also be prescribed in some cases.
Lifestyle Factors:
Lifestyle choices play a crucial role in managing chronic inflammation. Eating a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods (e.g., fruits, vegetables, fatty fish), regular exercise, stress management, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can help reduce inflammation.
Causes of Chronic inflammation:
Chronic inflammation can result from a complex interplay of factors. Here’s a detailed
Explanation of some common causes:
Persistent Infection:
Chronic infections by bacteria, viruses, or other pathogens can trigger ongoing inflammation. Conditions like tuberculosis, hepatitis, or periodontitis can lead to chronic inflammation if not effectively treated.
Autoimmune Diseases:
Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and Crohn’s disease occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues, leading to chronic inflammation.
Obesity:
Adipose tissue, especially visceral fat, produces inflammatory molecules. Excess fat can lead to a state of chronic low-grade inflammation, contributing to conditions like type 2 diabetes and heart disease.
Environmental Factors:
Long-term exposure to environmental toxins like air pollution, asbestos, or certain chemicals can lead to chronic inflammation. Smoking is a notable example.
Diet:
A diet high in processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats can promote inflammation. Conversely, a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids has anti-inflammatory effects.
Chronic Stress:
Prolonged stress triggers the release of stress hormones and inflammatory chemicals. This can contribute to chronic inflammation and worsen conditions like depression and anxiety.
Genetics:
Some individuals may be genetically predisposed to chronic inflammatory conditions. Certain genetic mutations can affect the regulation of the immune system, increasing the risk.
Autoinflammatory Disorders:
These are genetic conditions where the immune system becomes dysregulated, causing recurrent bouts of inflammation without an apparent trigger.
Tissue Injury:
Repeated tissue injuries or unresolved acute inflammation can transition into chronic inflammation. This can happen in conditions like osteoarthritis.
Aging:
As people age, their immune system may become less efficient at resolving inflammation, leading to a higher likelihood of chronic inflammation-related diseases.
Gut Dysbiosis:
An imbalance in the gut microbiome can lead to chronic inflammation. Conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) are examples.
Reduce Inflammation Naturally:
Reducing chronic inflammation naturally involves adopting a holistic approach to lifestyle, including dietary changes, exercise, stress management, and adequate sleep. Here’s a detailed guide:
Anti-Inflammatory Diet:
Focus on whole, unprocessed foods like fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins.
Incorporate foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids like fatty fish (salmon, mackerel), flaxseeds, and walnuts.
Reduce or eliminate processed foods, sugary drinks, and refined carbohydrates.
Include spices like turmeric, ginger, and garlic known for their anti-inflammatory properties.
Hydration:
Drink plenty of water to keep your body hydrated, as dehydration can exacerbate inflammation.
Manage Stress:
Practice stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, or mindfulness to lower chronic stress levels.
Regular Exercise:
Engage in regular physical activity, aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
Include strength training to build muscle and boost metabolism.
Adequate Sleep:
Prioritize quality sleep, aiming for 7-9 hours per night. Poor sleep can increase inflammation.
Maintain a Healthy Weight:
Excess body fat can promote inflammation, so strive for a healthy weight through diet and exercise.
Limit Alcohol and Tobacco:
Reduce or eliminate alcohol consumption and avoid smoking, as both can contribute to inflammation.
Manage Chronic Conditions:
If you have underlying health conditions like diabetes or autoimmune disorders, work closely with your healthcare provider to manage them effectively.
Probiotics and Prebiotics:
Include foods rich in probiotics (e.g., yogurt, kefir) and prebiotics (e.g., onions, garlic) to support a healthy gut microbiome, which can influence inflammation.
Herbal Supplements:
Some herbal supplements like curcumin (from turmeric), ginger, and green tea extract have anti-inflammatory properties. Consult a healthcare professional before using them.
Avoid Food Allergens:
Identify and eliminate any food allergens or sensitivities that may contribute to inflammation. An elimination diet or allergy testing can help with this.
Stay Hydrated:
Drink plenty of water throughout the day to help flush toxins from your body and maintain overall health.
S P E C I A L.
INCLUDE IN YOUR DIET.
1.FLAXSEED OIL,SEAWEED AND ALGAE.
2.BERRIES,CHERRIES AND APPLES.
3.WALNUTS ,CHIA SEEDS,HEMP SEEDSAND KIDNEY BEANS.
4.SWEET POTATO,BROCCOLI AND DARK GREEN LEAFY VEGETABLES.
5.TURMERIC AND GINGER .FRESH OR DRIED.
FAQ on chronic inflammation :
Q What is chronic inflammation?
A Chronic inflammation is a long-term, persistent immune response that can harm the body over time. It’s different from acute inflammation, which is the body’s short-term response to injury or infection.
Q What are the common causes of chronic inflammation?
A Common causes include poor diet, lack of exercise, smoking, excessive stress, and underlying health conditions like obesity or autoimmune diseases.
Q How does diet contribute to chronic inflammation?
A Diets high in processed foods, sugar, saturated fats, and trans fats can promote inflammation. In contrast, a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and omega-3 fatty acids can help reduce inflammation.
Q Can chronic stress lead to inflammation?
A Yes, chronic stress can trigger inflammation. Stress hormones like cortisol can promote inflammation when they’re constantly elevated.
Q Are there natural ways to reduce chronic inflammation?
A Yes, natural methods include adopting an anti-inflammatory diet, regular exercise, managing stress through techniques like meditation or yoga, getting enough sleep, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol.
Q What role does exercise play in reducing inflammation?
A Regular physical activity can help lower chronic inflammation by improving circulation, reducing fat tissue, and releasing anti-inflammatory compounds called cytokines.
Q Can certain foods help fight chronic inflammation?
A Yes, foods like berries, fatty fish (e.g., salmon), leafy greens, nuts, and turmeric have anti-inflammatory properties and can be beneficial.
Q Are there any supplements that can help with inflammation?
A Some supplements like omega-3 fatty acids, curcumin (from turmeric), and probiotics may have anti-inflammatory effects. Consult a healthcare professional before taking supplements.
Q How can I track my inflammation levels?
A You can measure inflammation markers in your blood, such as C-reactive protein (CRP) or erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), through a blood test. Consult your healthcare provider for testing and interpretation.
Q Can chronic inflammation be completely removed naturally?
A While natural methods can help reduce chronic inflammation but must consult health care consultant.
{NUTRITION LIFE CIRCLE} 

My Self Hari singh choudhary
S.N.H.S. Dip.(Holistic nutrition), London, S.N.H.S. Dip. (Advanced Nutrition), London, S.N.H.S. Dip. (Holistic Pain Management), London, S.N.H.S. Dip. (Nutrition for Age 50+), London, S.N.H.S. Dip. (Plant-Based Nutrition), London, S.N.H.S. Dip. (Vegetarian & Vegan Nutrition,) London, Certified Diabetes Educator’s (INDO-VIETNAM MEDICAL BOARD, Associate member of The International College of Holistic Medicine, England.
NATURAL DISEASE ERADICATION
[ NUTRITION THERAPY ]
For Business inquiry:-
Email: nutritionlifecircle@gmail.com
WhatsApp Number: +91 9425090558